CI/CD is one of the basic methods of continuous delivery concept. Gitlab offers the Pipelines module that implements CI/CD.
We are going to show how easy is to integrate Gitlab with Kubernetes. That integration will allow us to deploy a new version of the app to the K8S cluster right after a commit.
⚠️Warning We are assuming that you have basic knowledge of Kubernetes management.
Requirements
➡️ Gitlab instance (on-premise or cloud)
➡️ Shell runner
➡️ with Docker installed
➡️ K8S cluster (f.e. minikube)
Connecting to the cluster
To connect to the K8S cluster and be able to deploy objects (like pods or deployments), we need to configure the authorized connection using kubectl tool. Kubectl is basic for managing K8S cluster from the local computer. Unfortunately, placing configuration directly in the runner machine is not a good idea - everyone who can access the machine will be able to connect to our cluster or steal credentials (from ~/.kube/config file for instance).
Our savior is Docker and an image that exposes kubectl. The container needs to run only once (and delete itself afterward), configure the connection, and perform desired changes to the cluster. All of the sensitive data will be stored on the Gitlab side. and the runner will fetch them only during pipeline execution (as env variables).
ServiceAccount configuration for K8S
As the first, step we will create Service Account with proper permissions applied. The cluster API server is protected by JWT which is auto-generated once the account is created.
⚠️Warning To keep the article simple, we are ommiting details of RBAC.
To create and set up an account, we need to create some of the K8S objects. As an admin, run the following yaml with k apply -f path_to_file:
ℹ️ Hint
kis alias ofkubectl
> k apply -f /path/to/yaml/with/content/below.yaml
Contents of /path/to/yaml/with/content/below.yaml:
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: gitlab-deployment
namespace: development
---
kind: Role
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: gitlab-namespace-admin
namespace: development
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources: ["*"]
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- create
- update
- patch
- delete
- apiGroups:
- extensions
- apps
- networking.k8s.io
resources:
- deployments
- replicasets
- ingresses
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- update
- patch
- create
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: gitlab-development-admin-binding
namespace: development
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: gitlab-namespace-admin
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: gitlab-deployment
namespace: development
As the result, a service account called gitlab-deployment is created with permissions to deploy apps within namespace development.
Getting HWT assigned to the service account
The values of JWTs assigned to service accounts are stored in secrets. We need to figure out the secret name first that is used by the service account gitlab-deployment.
To do that we need to describe our service account i find out the proper name:
[root@k8s-master accounts]> k describe serviceaccount gitlab-deployment -n development | grep token
Mountable secrets: gitlab-deployment-token-mltnn
Tokens: gitlab-deployment-token-mltnn
As you can see, in our case the name of the secret is gitlab-deployment-token-mltnn. We can get the value now:
[root@k8s-master accounts]> k describe secret gitlab-deployment-token-mltnn -n development | grep "token:"
token: eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsImtpZCI6IjBhZTZrV3Z0eG8tQm95Z...........
Cluster certificate
Apart from JWT (authorization), we need to know a CA certificate used by K8S. We can get its value (as base64 encoded string) by running the following command:
⚠️Warning: this is a basic way to connect to the cluster - we recommend generating a separate client certificate issued by CA.
[root@k8s-master accounts]> cat /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf | grep certificate-authority-data:
certificate-authority-data: LS0tLS1CRUdJTiBDRVJUSUZJQ0FURS0tL.....
Deployment definition
We are ready to prepare a deployment object of our app:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: my-app-deployment
namespace: development
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: my-app
replicas: 1
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: my-app
spec:
containers:
- name: my-app
image: %IMAGE_NAME%
ports:
- containerPort: 80
imagePullSecrets:
- name: gitlab-container-registry
Pay attention to the two things, please:
1️⃣We are using placeholder %IMAGE_NAME% for docker image name - we need to replace it with the proper name before applying to K8S
2️⃣imagePullSecrets - remember to configure the cluster to access a private container registry - named gitlab-container-registry in this example (docs)
For this article, we will use a container registry hosted by Gitlab.
We are assuming that deployment definition will be placed in file ./deployments/deployment.yaml (path relative to git repository root).
Executing actual deployment
As for now, we are ready to perform the actual deployment.
Let's prepare a script (f.e. ./deployments/k8s.sh) which will be executed inside a container hosted on GitLab runner. It needs to use kubectl that will be available inside the container to open the K8S connection and perform all specified tasks:
kubectl config set-cluster k8s --server=$K8S_SERVER
kubectl config set clusters.k8s.certificate-authority-data $K8S_CERT
kubectl config set-credentials gitlab-deployment --token="${K8S_TOKEN}"
kubectl config set-context default --cluster=k8s --user=gitlab-deployment --namespace=$K8S_NAMESPACE
kubectl config use-context default
echo "Applying objects to k8s"
kubectl apply -f /deployment.yaml
Steps (keep in mind that all the commands will be executed inside container):
- We set cluster address from
K8S_SERVERenv variable (so we need to pass its value from runner job to the container) and set its name tok8s - We set CA cert
- Then JWT value
- We set default service account/namespace/cluster name w kubectl
- We apply K8S objects defined in
/deployment.yamlfile (so we need to pass it to the container as well)
Gitlab pipeline
We are ready to define Gitlab pipeline (.gitlab.yml), finally. As image registry, we will use the already mentioned container registry. It is integrated into the gitlab project very well and we don't need to worry about logins/password/image names as Gitlab will prepare all values as predefined environment variables.
Our pipeline needs to be split into two stages: image building and K8S deploy:
stages:
- build
- deploy
Before specifying jobs for the stages, we can prepare one useful variable available across all of the jobs:
before_script:
- IMAGE_NAME="${CI_REGISTRY_IMAGE}:$(echo $CI_COMMIT_REF_SLUG)-$(echo $CI_COMMIT_SHORT_SHA)"
To build IMAGE_NAME we use a couple of Gitlab predefined variables. As a tag, the last commit short sha and branch name are used.
ℹ️ Hint Sample image name built according to the pattern above:
git.my-company.com:5050/pwasiewicz/my-app:develop-29790ef3
Stage: build
So, we are ready to build and push an image to the image registry.
build-image:
stage: build
only:
- develop
script:
- docker build -f ./path/to/Dockerfile -t $IMAGE_NAME .
- docker login -u $CI_REGISTRY_USER -p $CI_REGISTRY_PASSWORD $CI_REGISTRY
- docker push $IMAGE_NAME
1️⃣ We are building the image from Dockerfile placed in code repository and named IMAGE_NAME
2️⃣We are logging into container registry - Gitlab offers predefined variables as mentioned before
3️⃣the image is pushed
Stage: deploy
We are missing the deploy job only:
deploy-k8s-dev:
stage: deploy
environment: Development
only:
- develop
script:
[scripts are described below]
Firstly, we need to replace the placeholder in ./deployments/deployment.yaml proper image name. We will use sed command. We do not need to worry about file modifications as runner resets git repository to clean state before every job run.
- sed -i "s/%IMAGE_NAME%/$(echo $IMAGE_NAME | sed -e 's/[\/&]/\\&/g')/g" ./deployment/deployment.yaml
Secondly, we need to run the container with kubectl tool and runsthe script we have prepared before (inside container) that will do connection and deploy things for us:
- |
docker run
-i --rm
--env-file <( env | cut -f1 -d= | grep "^K8S_" )
-v ./deployments/deployment.yaml:/deployment.yaml
-v ./deployments/k8s.sh:/deploy-k8s.sh
dtzar/helm-kubectl /bin/sh /deploy-k8s.sh
Tips:
--env-file <( env | cut -f1 -d= | grep "^K8S_" )- we are passing all env variables that names start withK8S_from runner to the container - we will set their values directly in Gitlab project so the runner will grab them before job start-v ./deployments/deployment.yaml:/deployment.yaml- we need to mountdeployment.yamlfrom our host (runner)-v ./deployments/k8s.sh:/deploy-k8s.sh- the same withk8s.shdtzar/helm-kubectl /bin/sh /deploy-k8s.sh- execute mounted script (entry point)
The whole contents of .gitlab.yml:
stages:
- build
- deploy
before_script:
- IMAGE_NAME="${CI_REGISTRY_IMAGE}:$(echo $CI_COMMIT_REF_SLUG)-$(echo $CI_COMMIT_SHORT_SHA)"
build-image:
stage: build
only:
- develop
script:
- docker build -f ./path/to/Dockerfile -t $IMAGE_NAME .
- docker login -u $CI_REGISTRY_USER -p $CI_REGISTRY_PASSWORD $CI_REGISTRY
- docker push $IMAGE_NAME
deploy-k8s-dev:
stage: deploy
environment: Development
only:
- develop
script:
- sed -i "s/%IMAGE_NAME%/$(echo $IMAGE_NAME | sed -e 's/[\/&]/\\&/g')/g" ./deployment/deployment.yaml
- |
docker run
-i --rm
--env-file <( env | cut -f1 -d= | grep "^K8S_" )
-v ./deployments/deployment.yaml:/deployment.yaml
-v ./deployments/k8s.sh:/deploy-k8s.sh
dtzar/helm-kubectl /bin/sh /deploy-k8s.sh
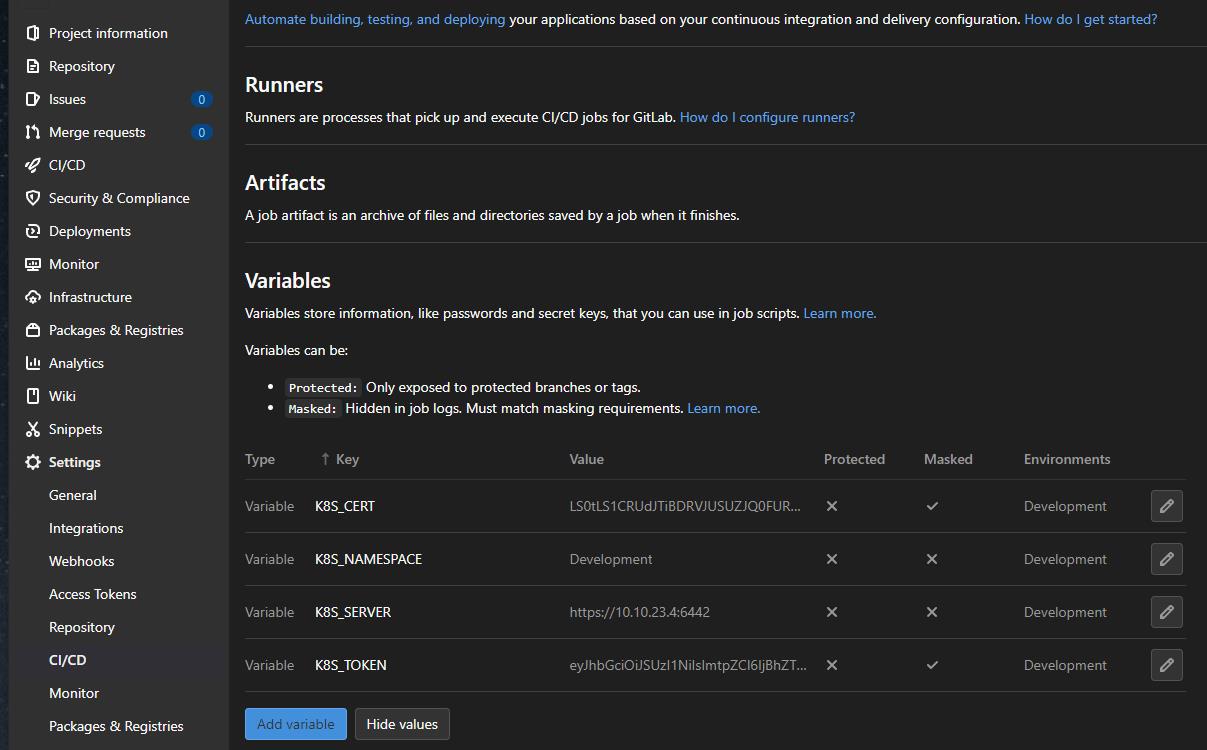
Variable configuration
The last step is to set proper variables in the Gitlab proejct settings:
Summary
In this article, we showed how to deploy an app using Gitlab Pipeline into Kubernetes quite easily.
It is great base for further improvements:
- you can extract part of scripts to a separate project and download them directly in the pipeline definition - it will allow sharing deployment scripts across projects.
kustomizesupport - you can write scripts that will run kustomization before applying objects to the cluster - so you can store project-related K8S objects configuration in a project repository